Stages of work on the project


1. Stage - Analysis of CA
The average age and gender of users, their interests and goals with which they visit the site or application, geography of residence - all this information helps to create a portrait of the target audience. Thanks to it, it is easier for the designer to predict the behavior people and create the most convenient product for them.
Let’s imagine that a UX/UI designer is working on an application for an aggregator of plane and train tickets in Ukraine and around the world.
The target audience can be presented in the following way:
- Gender: men and women.
- Age: 18-55 years.
- Geography of residence.
- Income: average, higher than average.
- Marital status: single, couples, families with children.
- Interests: travel, tourism, active lifestyle, business.
- Purposes of using the program: quick search for tickets, the ability to find the optimal price and route.
If you finish the CA analysis in this form, the audience of the product will turn out to be too broad, it will be difficult for a specialist to create a program especially for her. Therefore, you can divide the audience into segments:
- Students aged 18 to 24: with a low income use the application infrequently — during the holidays, give preference for budget options.
- Businessmen aged 25 to 45: with above-average income, travel often for business trips and meetings, use high class planes or trains.
- Families with or without children: average-above-average income, age of spouse or parents - 25-45 years old, use the application several times a year - on long holidays, during holidays and vacations.

2. Stage - Analysis of competitors
Studying the strengths and weaknesses of competitors helps the UX designer to improve the product without repeating the mistakes of colleagues. At this stage, you can analyze the sites and programs of not only competing companies, but also those engaged in related business. For example, if you work with a network of fitness centers, you should pay attention to the interfaces of sports nutrition stores or clothes

3. Stage - Defining the structure
At this stage, the main sections of the product are created, their interaction and location are determined. Design correctly the structure of the site or program will be helped by information architecture. It determines what data should be placed on each page and how to link them to each other so that the product content becomes convenient and logically related to users.
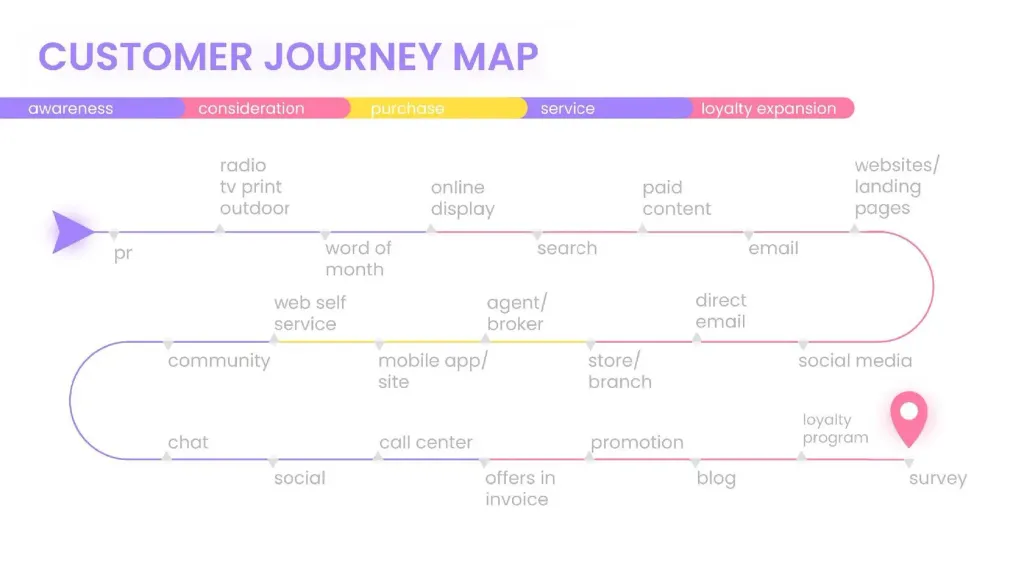
At this stage, a Customer Journey Map can also be created. At its core, CJM is visualization interaction of the consumer and the product from the user’s point of view. In the map, the designer describes the ways in which the client came to the site, what barriers he faced, what he is afraid of and why he may refuse to buy. With the help of CJM is formed structure of the future project.
4. Stage - Creating a prototype
Prototyping is a very important stage of product development. This is where the work on UI design begins. Prototype tests the target audience of the project, demonstrate it to the customer or shareholders, attract investors with its help.
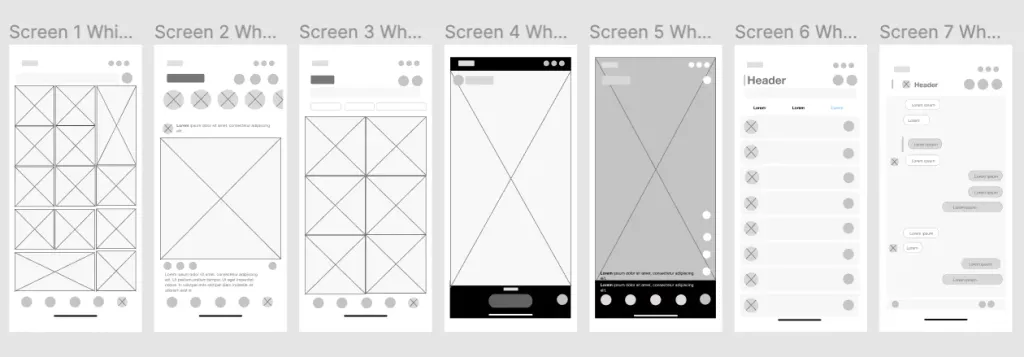
To begin with, the designer creates a wireframe (from the English Wireframe - “framework”) - a diagram that reflects the general concept of the product and its main sections. Wireframe is distinguished by monochromeness and low level of visualization. You can say that it is simplified an image of the site or application that contains all the elements of the product. A wireframe shows how the interface works and interacts with it user.
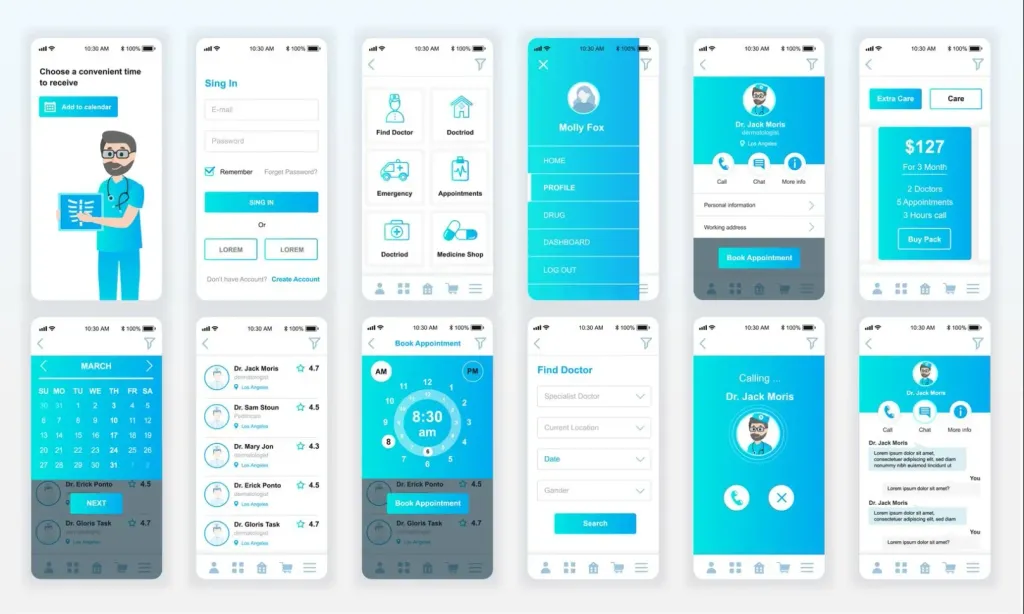
After the wireframe, the specialist starts creating the layout. At this stage, the interface is filled with logos, colors, and pictures and texts - the design of the future product becomes more detailed. A mockup helps the client and the team appreciate the visual component of the site or program.
Finally, the designer creates a full-fledged model of the product - an interactive prototype. It includes all content of the site or application: users can click buttons, navigate from page to page, and see how product features work.
5. Stage - Testing
A prototype contains all the visual and functional elements of a site or application, so it is tested for detection before release errors and improvement of the final result.
There are two types of testing: quantitative and qualitative. In the first case, research is conducted on a large sample of users, in the second, a focus group from CA is involved in the case.
Feedback is very important for a UX/UI designer, because even a seasoned professional can get things wrong client behavior. What mistakes did you make during development, what features are better to replace, is the interface clear to users, how quickly they achieve their goal, do they have comments on the product, answers to these and other questions are provided by testing. It can be conducted using Google Forms, Maze or Quant-UX.
After testing is completed, UX/UI specialists work on finalizing the site or application. The product may go to the market before it is released several of its prototypes.

6 Stage - Product support and development
The release of a site or application does not mean that work on the project is finished. Some time after the release, the designers test again product, improve it and make it more effective for users. Often sites and applications get new features, sometimes they need a redesign.
