How to make a UX review of your product?

What is a UX review and why is it important to implement this process in your product? How to analyze the product yourself, discover pains and problems of the user? How to properly prioritize test results and implement them in life?
Natalya Shevchenko is a product designer of the Yoga-Go application from Welltech. In the author’s column, she decided to share with her own experience of conducting a UX-review of an application, and prepared a step-by-step guide that you can use for your products.

What is UX-review?
UX-review is a process of checking the user experience of a current product to find its potential problems, “pain points” users and suggest improvements. UX-review is carried out by an internal team or engaged third-party specialists. In this material, we will focus on how a designer can independently carry out such a process.
Why is this important?
UX-review is a tool that helps to make an action plan with changes in the product. This helps to increase the level of satisfaction users from the application, and even contribute to increased conversions and revenue growth. It’s cool if the product has it a planned activity that takes place regularly to improve metrics and user experience. So UX-review is important stage in product improvement.
When you work on one case for a long time, the problem of “cloudy eye” arises, when it is difficult to notice the real needs of users and flaws in product logic. There are several UX-review methods that can be used to analyze a product. I will list the main ones:
-
Expert Review: This method is used to evaluate the logic of the product from the perspective of UX experts. Experts analyze the product, taking into account its target audience, context of use, interaction with the user and other aspects. Expert review can be useful in combination with other methods.
-
Heuristic analysis is used to identify typical product usage problems. In this method, one or more experts compare the product design to a list of predetermined design principles, and discover where the product falls short corresponds to them.
-
Usability testing: this method consists in testing the product on users in order to identify problems with which they encountered when interacting with the product.
-
Product data analysis: this method is used to analyze the data that is collected from the product (analytics, feedback and user comments, NPS, etc.) to identify trends and issues in product interactions.
These methods can be combined and used in various combinations to achieve maximum efficiency in UX-review product While researching Yoga-Go’s problem areas, I focused on usability testing with our users, mixing with by other methods. Conducting a UX-review may include the following steps:
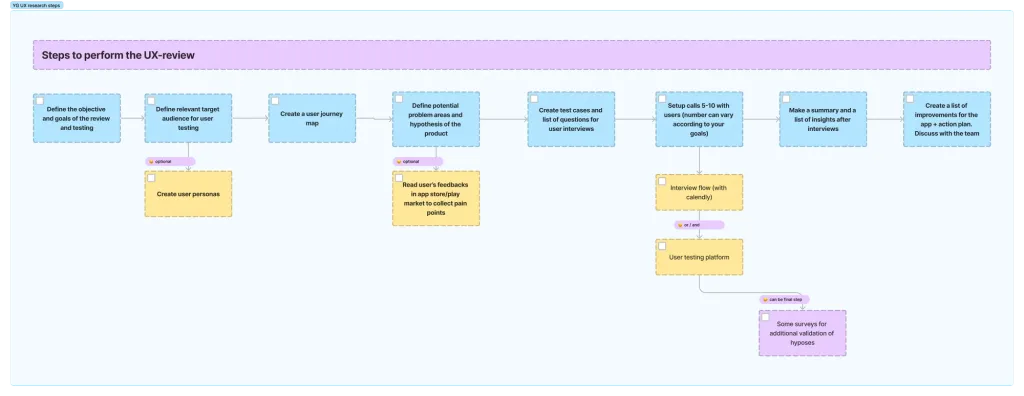
- Defining the main goals you want to achieve with the help of UX-review.
- Determination of the target audience that will be most relevant for usability testing.
- Creation of CJM.
- Identification of potential problem areas of the product and formation of hypotheses.
- Creation of test cases and questions for users.
- Setup of interviews with users.
- Summarizing and creating a list of improvements for the product.
- Presentation of results to the product team and summary.
Goals for UX-review and usability testing
I think that this step is understandable. First of all, you need to define the research objectives and discuss them with the team. What exactly do you want to know as a result of the test? What problems or shortcomings do you want to identify? It is important that research objectives correlated with product, business and user needs. It would be helpful to brainstorm with the team to determine and discussion of the main goal.
Defining the target audience
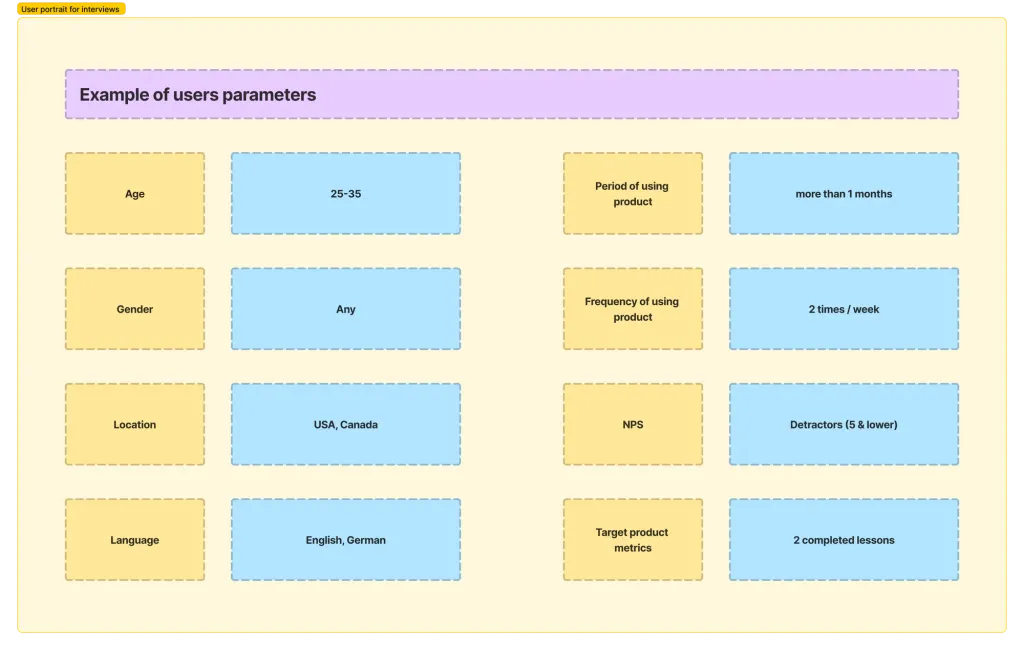
When conducting a UX-review, in my opinion, it is important to focus on your existing audience, and not on new users. In this way, communication will be more effective, because users have already formed a certain opinion about your product. To determine the target audience before conducting UX research, it is important to research the profile of the product’s user or view analytics, to check the basic parameters of your audience. Here is a list of basic audience parameters that are important to consider when research preparation: gender, target location, age, language.
It is also important to identify additional CA parameters of your product that may affect the study, for example:
- period of use of the application/product;
- frequency of product use;
- the number of execution of the target action in the product;
- NPS rating;
- or others relevant to your product.
Creating a Customer Journey Map and forming hypotheses
CJM is extremely useful before testing because it allows you to decompose the user experience over time use of the product and look more broadly at the product. Analyzing the user journey can reveal areas for improvement interaction with the product. For example, to identify “pain points” or inaccuracies in logic. This information may be used for creating specific questions and a test script, focusing on possible problem areas. It is difficult to ask about everything immediately, especially when there is little time for the interview.
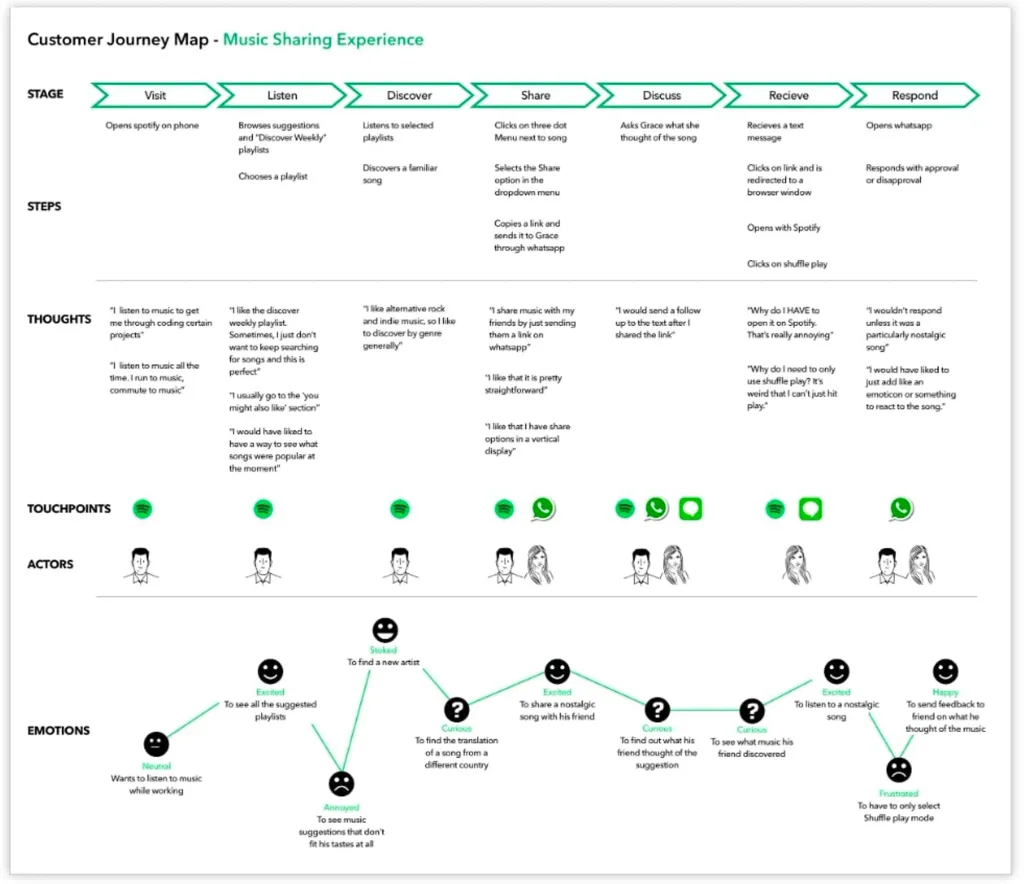
After creating a CJM, it is important to identify possible product “pain points” and generate hypotheses for research. This will help create quality test script and user questions. One approach to creating hypotheses is to categorize them by different sections of the product, which allows you to prepare specific questions. For example, while working on the Yoga-Go review, I selected the following categories for forming hypotheses: personal plan; a collection of yoga series; player; additional questions
Creation of test cases and questions for users
Create a list of tasks that users will need to complete during testing. Tasks should be realistic and related to product functionality. The interview with Yoga-Go users consisted of two parts: remote testing of the product (according to the user tasks) and general questions about the product experience. Here are some tips to help you write an interview script:
-
Try to fit the interview into 30 minutes. In my experience, 30-minute interviews are optimal. They can be longer tiring for both the interviewer and the respondent.
-
Break the questions into blocks. For example, according to the categories that you defined earlier and estimate the time for each block.
-
Try to “run” the script on several colleagues to understand whether all the questions are clear and fit into the established timing.
-
It is important to compare the interview script with the CJM to ensure that all the problem areas are covered in the test and filter unnecessary questions.
-
Throughout the interview process, focus on your hypotheses.
Organization and conduct of interviews
For the UX-review of our application, we were looking for participants among current users. With the help of analytics, we selected users who meet the parameters from the section above (definition of CA) and sent them an invitation to an interview by e-mail addresses Unfortunately, the conversion of conducting interviews is quite low (the number of conducted interviews, compared to the number of sent letters), but you can make several mailings, depending on the required number of respondents.
The most important part of the research process is conducting the interviews themselves. During the meeting, it is important to take notes (or better session recording) and correlate them with your hypotheses. This helps to focus on the research objectives, because from the users you can hear many ideas and opinions. Here are some tips to keep in mind when interviewing:
-
Conduct no more than 3-4 interviews per day;
-
Create a board in FigJam or Miro to record notes, insights and track progress;
-
Invite a colleague, for example a product manager or another designer, to the first few interviews to feel more confident;
-
You should not push the user to answers that will confirm hypotheses, try to listen more and only ask clarifying questions;
-
Do not worry if the respondent did not show up - this is a common phenomenon during interviews.
Creating a list of enhancements for the product
Debriefing after user interviews involves analyzing the data collected during the interviews and identifying key findings that can form the basis for future product improvements. Here are some steps to optimize your recap:
-
Review the notes you took during the interviews and highlight important points.
-
Identify patterns: Look for common themes or issues that emerged from the interviews you conducted.
-
Organize data: group data into categories based on themes or issues that have been identified.
-
Compare the insights you discover with the hypotheses you created at the beginning and CJM to understand what was confirmed and what was not.
-
Create an action plan with specific steps to improve your app’s user experience.
-
Break it down into tasks and prioritize them, depending on the needs of the product. I used the RICE method for evaluation and prioritization of tasks (FigJam template).
Conclusion
As a result of the UX-review of the Yoga-Go application, we confirmed several hypotheses regarding gaps in the functionality of the product, found inaccuracies in logic and revealed additional pain points of users. After that, together with the team, they drew up a clear action plan and created it tasks to work on the most priority problems. After implementing the improvements, it would be useful to perform another cycle interviewing users to verify the effectiveness of the changes made and their impact on the product.
After summarizing and designing the final result, it is important to share the research with the product team, discuss the action plan and plan future updates to the product. Remember that improvements should be based on data, collected during interviews, and should help address identified needs and improve user experience. Finally, step-by-step checklist for UX-review:
-
Determination of the main goals of UX-review;
-
Determination of the target audience for usability testing;
-
Creation of CJM;
-
Identification of potential problem areas of the product and formation of hypotheses;
-
Creation of test cases and questions for users;
-
Organization of interviews (e.g. email newsletter);
-
Conducting interviews;
-
Summarizing and creating a list of improvements for the product;
-
Presentation of the results to the product team and discussion of the further action plan.
